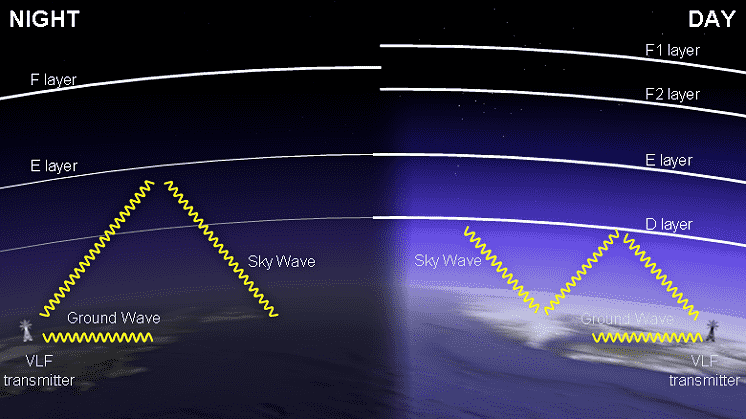
The ionosphere is divided meteorologically into different regions or layers and each layer exhibit different characteristics.
The layers of the ionosphere are:
- D-Layer
- E-Layer
- Es-Layer
- F1-Layer
- F2-Layer
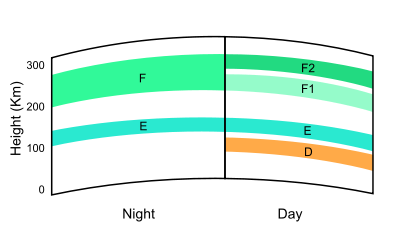
1. Characteristics of D-Layer:
- It is the lowest layer of the ionosphere.
- It exists at an average height of 70 km.
- Its thickness is 10 km.
- It exists only in day-time.
- Its ionization properties depend on the altitude of the sun above the horizon.
- It is not a useful layer for HF communication.
- It reflects some VLF and LF waves.
- It absorbs MF and HF waves to some extent.
- Its electron density, N = 400 electrons/cm3.
- Its virtual height is 60 to 80 km.
- Critical frequency of the layer, fc = 180 kHz.
2. Characteristics of E-Layer:
- It exists next to D-Layer.
- It exists at an average height of 100 km.
- Its thickness is about 25 km.
- It exists only in day-time.
- The ions are recombined into molecules due to the absence of sun at night.
- It reflects some HF waves in day-time.
- It disappears at nights.
- Its electron density, N = 2 × 105 electrons/cm3.
- Its virtual height = 110 km.
- Its critical frequency, fc ≈ 4 MHz.
- Maximum single-hop range ≈ 2350 Km.
3. Characteristics of Es-Layer:
- It is a sporadic E-Layer.
- Its appearance is sporadic in nature.
- If at all it appears, it exists in both day and night.
- It is a thin layer.
- Its ionization density is high.
- It appears close to E-Layer.
- If it appears, it provides good reception.
- It is not a dependable layer for communication.
4. Characteristics of F1-Layer:
- It exists at a height of about 180 km in day-time.
- Its thickness is about 20 km.
- It combines with F2-Layer during nights.
- HF waves are reflected to some extent.
- It absorbs HF to a considerable extent.
- It passes on some HF waves towards F2-layer.
- It’s virtual height ≈ 180 km.
- Its critical frequency, fc ≈ 5 MHz.
- Maximum single-hop range ≈ 3,000 km.
5. Characteristics of F2-Layer:
- It is the most import layer for HF communication.
- Its average height is about 325 km in day-time.
- Its thickness is about 200 km.
- It falls to a height of 300 km at nights as it combines with the F1-Layer.
- The height of F2-Layer varies drastically with the time of the day, the average ambient temperature and sunspot cycle.
- It exists at nights also.
- It is the topmost layer of the ionosphere.
- It is highly ionized.
- It offers better HF reflection and hence reception.
- Electron density of F-Layer, N = 2 × 106 electrons/cm3.
- Its virtual height = 300 km in day-time and 350 km in the night.
- Its critical frequency, fc ≈ 8 MHz in day-time and fc ≈ 6 MHz at nights.
- Maximum single-hop range ≈ 3,800 km during day-time and 4,100 km at night.

Antenna arrays full notes