Need of Sampling and Quantization in Digital Image Processing:
Mostly the output of image sensors is in the form of analog signal. Now the problem is that we cannot apply digital image processing and its techniques on analog signals.
This is due to the fact that we cannot store the output of image sensors which are in the form of analog signals because it requires infinite memory to store a signal that can have infinite values. So we have to convert this analog signal into digital signal.
To create a digital image, we need to convert the continuous data into digital form. This conversion from analog to digital involves two processes: sampling and quantization.
Quantization -> digitization of amplitude values
Sampling in Digital Image Processing:
- In this we digitize x-axis in sampling.
- It is done on the independent variable.
- For e.g. if y = sinx, it is done on x variable.
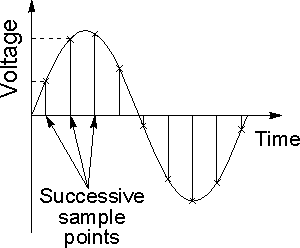
- There are some variations in the sampled signal which are random in nature. These variations are due to noise.
- We can reduce this noise by more taking samples. More samples refer to collecting more data i.e. more pixels (in case of an image) which will eventually result in better image quality with less noise present.
- As we know that pixel is the smallest element in an image and for an image represented in the form of a matrix, total no. of pixels is given by:
- The number of samples taken on the x-axis of a continuous signal refers to the number of pixels of that image.
- For a CCD array, if the number of sensors on a CCD array is equal to the number of pixels and number of pixels is equal to the number of samples taken, therefore we can say that number of samples taken is equal to the number of sensors on a CCD array.
- Oversampling is used for zooming. The difference between sampling and zooming is that sampling is done on signals while zooming is done on the digital image.
Quantization in Digital Image Processing:
- It is opposite of sampling as sampling is done on the x-axis, while quantization is done on the y-axis.
- Digitizing the amplitudes is quantization. In this, we divide the signal amplitude into quanta (partitions).
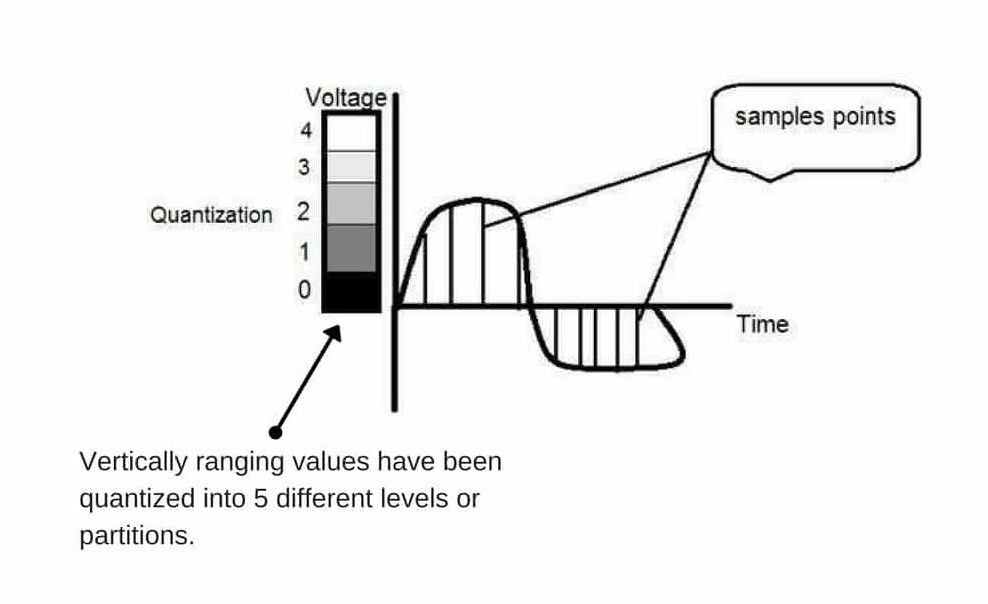
Relation of Quantization and gray level resolution:
- Number of gray levels here means number of different shades of gray.
- To improve image quality, we number of gray levels or gray level resolution up.
- If we increase this level to 256, it is known as the grayscale image.
![]()
Where,
L = gray level resolution
k = gray level
Questions Asked:
Q1. What do you mean by Sampling and Quantization in Digital Image Processing?
Q2. Write a short note on Image Sampling and Quantization?

very helpful thank you so much for efforts
Very well explained 👍 👍
thanks. tis good.
NOW LET ME REPEAT AFTER YOU.
SAMPLING: NUMBER OF PIXELS (NUMBER OF LOCATIONS IN A CONTINUOUS IMAGE) WE TAKE FROM A SCENE.
QUANTIZATION : QUANTIFYING THE AMPLITUDE OF A LOCATION’S (OR PIXEL’S) COLOR VALUE.
Explained it very easy … Thanks
Very useful and crisp explanation. Thank you
how sampling and quantization affects the size of a digital image.