In image processing, it is defined as the action of retrieving an image from some source, usually a hardware-based source for processing. It is the first step in the workflow sequence because, without an image, no processing is possible. The image that is acquired is completely unprocessed.
Now the incoming energy is transformed into a voltage by the combination of input electrical power and sensor material that is responsive to a particular type of energy being detected. The output voltage waveform is the response of the sensor(s) and a digital quantity is obtained from each sensor by digitizing its response.
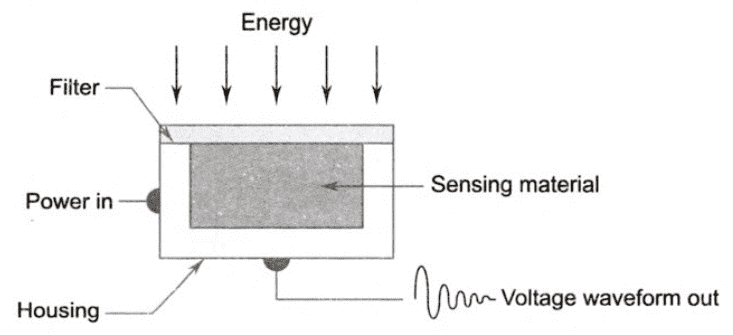

Image Acquisition using a single sensor:
Example of a single sensor is a photodiode. Now to obtain a two-dimensional image using a single sensor, the motion should be in both x and y directions.
- Rotation provides motion in one direction.
- Linear motion provides motion in the perpendicular direction.
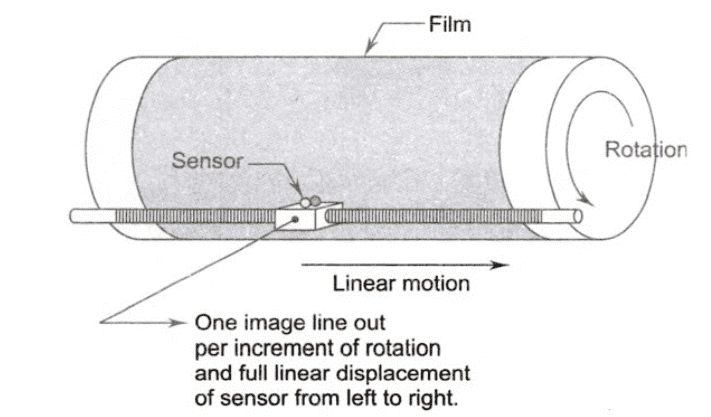
This is an inexpensive method and we can obtain high-resolution images with high precision control. But the downside of this method is that it is slow.
Image Acquisition using a line sensor (sensor strips):
- The sensor strip provides imaging in one direction.
- Motion perpendicular to the strip provides imaging in other direction.
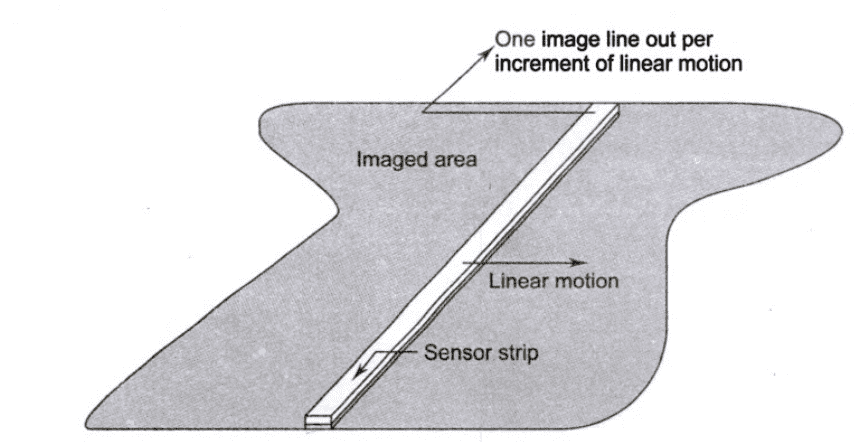
Image Acquisition using an array sensor:
In this, individual sensors are arranged in the form of a 2-D array. This type of arrangement is found in digital cameras. e.g. CCD array
In this, the response of each sensor is proportional to the integral of the light energy projected onto the surface of the sensor. Noise reduction is achieved by letting the sensor integrate the input light signal over minutes or ever hours.
Advantage: Since sensor array is 2D, a complete image can be obtained by focusing the energy pattern onto the surface of the array.
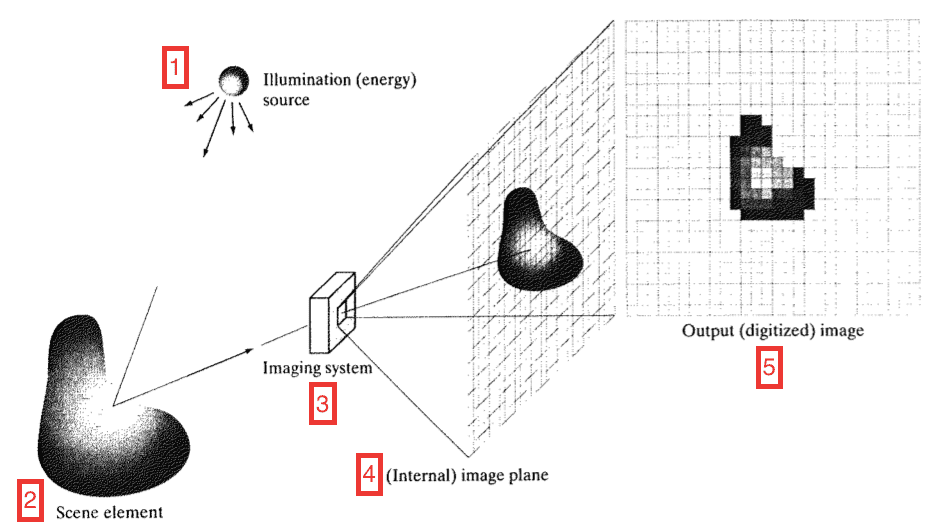
The sensor array is coincident with the focal plane, it produces an output proportional to the integral of light received at each sensor.
Digital and analog circuitry sweep these outputs and convert them to a video signal which is then digitized by another section of the imaging system. The output is a digital image.
References: Digital Image Processing By Rafael C. Gonzalez, Richard Eugene Woods
beautiful thanks
beautiful thanks!!!!!!!!!!!!!!111111
….
What exactly is meant by an imaging system