1. Simulation is the process of conducting experiments on a model of a system for the purpose of understanding or verifying the operation of the actual system.
2. REQUIREMENTS OF A VHDL SIMULATOR:
- A VHDL simulator must provide data structures and algorithms that allow it to efficiently simulate the execution of concurrent statements in a VHDL program.
- A simulator must also efficiently produce an accurate representation of the output waveforms that result from the application of a set of input values to the design entity being simulated.
3. During a simulation, changes in input and output signals occur in simulation time, the time value maintained by the simulator, as opposed to real time. Each change in the value of a signal is an event.
4. KINDS OF SIMULATORS:
Based on their approach to performing simulation, there are three common kinds of simulators for digital systems: time driven, event-driven, and cycle based.
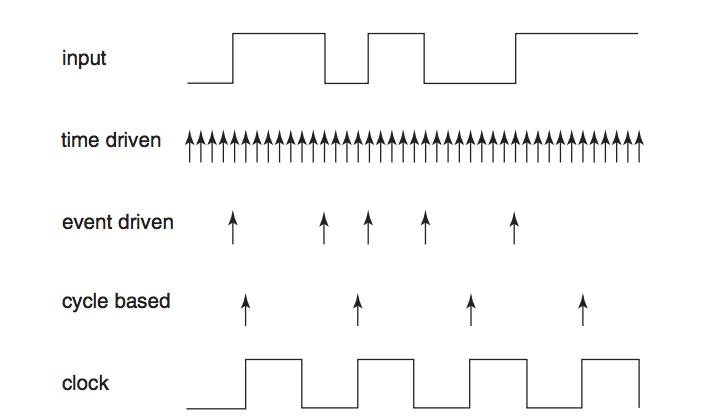
- Time-Driven Simulation:
- In the time driven simulation, simulation time is advanced in predetermined uniform increments.
- The fixed size of time step determines the resolution with which events can be observed. E.g. simulation time might be advanced in 1ns steps.
- As the time is advanced, any events in the next time step are simulated.
- There are a very large number of time steps during which there are no events in the time-driven simulation. Still, a time driven simulator must execute a simulation cycle for each time step.
- Event – Driven Simulation:
- In the event-driven simulation, time is advanced in non-uniform steps whose sizes depend on when the event occurs.
- It responds to each i/p event by executing a sequence of simulation cycles that determine when and to what values the simulated system’s signals change.
- Advantages:
- Eliminates the need for the simulator to evaluate the model at empty time steps (those without events) that are evaluated in time – driven simulation.
- Faster and more precise simulations.
- Cycle – Based Simulation:
- Faster than event-driven simulation.
- Only applicable to functional simulation of synchronous sequential systems that have a single clock.
- A cycle based simulator collapses the logic that determines FF i/p values in a sequential design into equations based on the present input values and present state of the system’s FF(s). Resulting model is evaluated only at triggering edge of each clock cycle.
- Since the execution of a model only at each clock triggering edge, it reduces simulation time. But all delay information is lost and only signal values at clock triggering edges are available.
Reference: VHDL for Engineers by Kenneth L. Short
