1. In an event-driven simulation, time is advanced in non-uniform steps whose sizes depend on when event occurs.
2. It responds to each i/p event by executing a sequence of simulation cycles that determine when and to what values the simulated system’s signals change.
3. Advantages:
- Eliminates the need for the simulator to evaluate the model at empty time steps (those without events) that are evaluated in time – driven simulation.
- Faster and more precise simulations.
4. An event-driven simulator performs three steps to accomplish a simulation:
- elaboration
- initialization
- repeated execution of simulation cycles
5. Elaboration:
- Elaboration is the creation of a simulation model for a design entity from its VHDL description.
- This simulation model resides in the host computer’s memory.
- This simulation model consists of a net (network) of simulation processes.
- During elaboration, all concurrent statements are converted to equivalent simulation processes.
- During elaboration, for each signal assigned a value in a simulation process, a signal driver is created. This signal driver is associated with the simulation process containing the signal assignment statement.
6. Initialization:
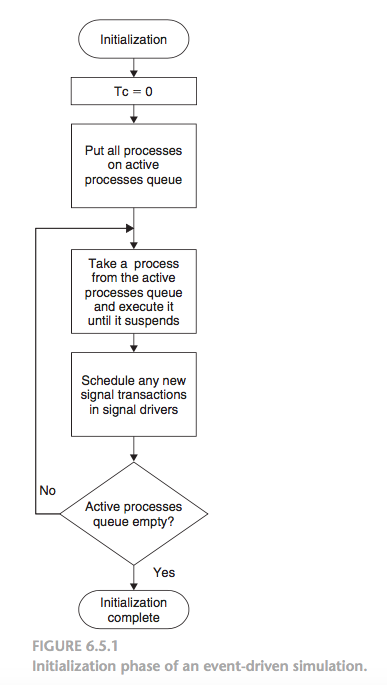
- After elaboration is completed, simulation consists of an initialization phase followed by repetitive execution of simulation cycles.
- At the beginning of the initialization phase, the current time (Tc) is set to 0
- The kernel places all of the simulation processes in the active processes queue. Each simulation process is then taken from this queue and executed until it suspends.
- A simulation process is suspended either implicitly or explicitly.
- A process with a sensitivity list is suspended implicitly after its sequential statements have been executed to the end of the process.
- A process with one or more wait statements is suspended explicitly when its first wait statement is executed.
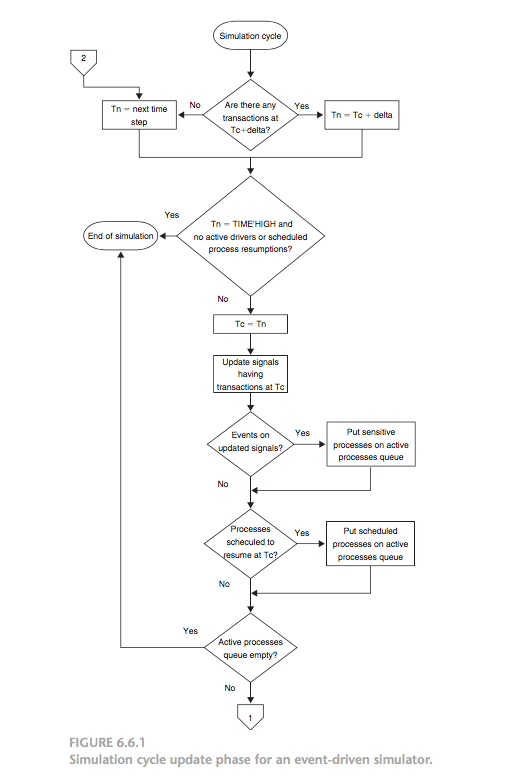
7. Simulation Cycles:
- After the initialization phase, all simulation processes are in their suspended states. The first simulation cycle is then executed.
- A simulation cycle consists of two phases:
- Update phase: The update phase first determines the next value for the current simulation time and advances the simulator clock to this value. Based on this new simulation time, a determination is made as to whether the simulation is complete.
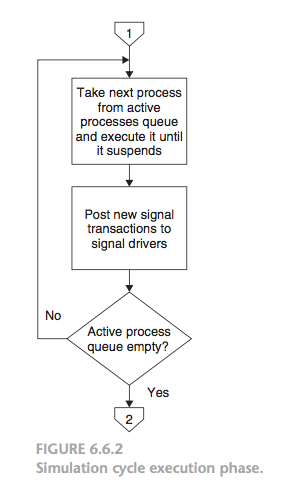
- Execution phase: During the execution phase, each simulation process in the active processes queue is taken from that queue and executed until it suspends.
- Update phase: The update phase first determines the next value for the current simulation time and advances the simulator clock to this value. Based on this new simulation time, a determination is made as to whether the simulation is complete.
Reference: VHDL for Engineers by Kenneth L. Short
